Human Population Increase During the Holocene Was Likely Due to
Second deep human history warns us that when climate patterns did change significantly the result was societal collapse war epidemics and fundamental restructurings of the geography and. Yr BP that took place in northern Europe is concurrent with the start of a massive increase in population levels.

A Comparison Between Pleistocene And Early Holocene To Present Day Download Scientific Diagram
The same pattern of pre-agricultural population growth is evident when reviewing the population reconstruction of Holocene Finland in its entirety Tallavaara et al Reference Tallavaara Pesonen and Oinonen 2010.
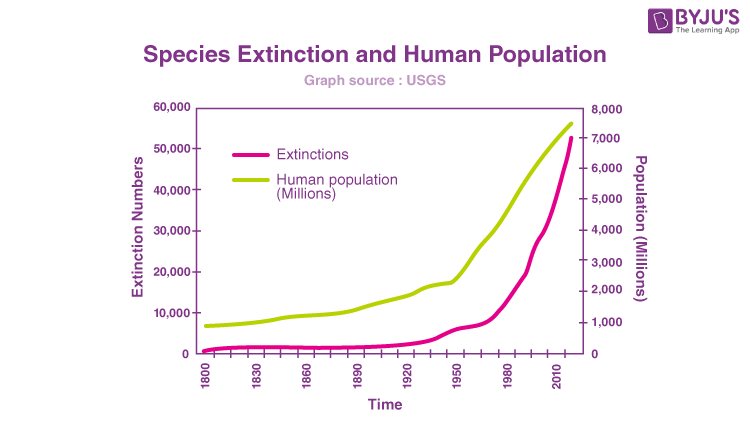
. Furthermore it has been suggested that the Anthropocene era actually started in the Middle Holocene due to increased generation of CH 4 from ancient rice agriculture and animal husbandry in China although this view has been disputed. Human impact has pushed Earth into the Anthropocene scientists say. Several studies have attempted to test and quantify this notion on a contemporary.
102-8 kya we identified a recovery of relative population levels when growth rates were similar or slightly greater than those of the first. Evidently the large climatic and environmental change at 6000 cal. Our results showed many population growth events that were likely due to the Neolithic Revolution ie the shift from hunting and gathering to agriculture and settlement.
The same rates of prehistoric population growth measured worldwide suggest that the global climate andor biological factors intrinsic to the species and not factors related to the regional environment or subsistence practices regulated the growth of the human population for most of the last 12000 y. Human overpopulation or human population overshoot is the concept of a human population becoming too large to be sustained by its environment or resources in the long term. The idea is usually discussed in the context of world population though it may also concern regionsHuman population growth has increased in recent centuries due to medical advancements and.
During the second half of the Early Holocene c. Following the relatively wet and stable climate of the Holocene. As a center of rice domestication and early population growth the lower Yangtze River has been extensively transformed in the Holocene.
The same rate of growth measured for populations dwelling in a range of environments and practicing a variety of subsistence strategies suggests that the global climate andor endogenous biological factors not adaptability to local environment or subsistence practices regulated the long-term growth of the human population during most of the Holocene. This represents a population growth rate of 61. Although caution is required in inferring actual population growth rates directly from rates of change in summed radiocarbon the latter values exceed 1 during this earliest phase are unlikely to be explained by increased fertility among farming groups alone and therefore must be due in part to migrant farmers from the European mainland a conclusion.
Using N isotope compositions from Irish terrestrial mammals from the Late Pleistocene through to the Late Holocene we. Population dynamics over the Maglemose and early Kongemose period are poorly understood but one can assume at least a gradual population increase as seen in other nearby areas during the Early. First for most of human history major crises and ruptures in human societies came as a result of climate change not because of too many people or human misuse of resources.
Dingo invasion in the Holocene regime shift on the mainland climate change and human intensification ie human population growth and technological advances on the mainland provide two alternative or synergistic explanations Lourandos 1997 John-son and Wroe 2003 Brown 2006. And a growth in population and consumption have driven the move. In some locations this could be true for winter as well.
Our results help to provide a clearer picture of human prehistoric demography confirming the significant impact of agriculture on population expansion and provide new hypotheses and directions for. Although caution is required in inferring actual population growth rates directly from rates of change in summed radiocarbon the latter values exceed 1 during this earliest phase are unlikely to be explained by increased fertility among farming groups alone and therefore must be due in part to migrant farmers from the European mainland a conclusion. Creased cloud cover during the mid-Holocene and warmer winters at high latitudes due to reduction of winter sea ice cover caused by more summer melting.
They suggest that when all of the regions experienced similar populations shifts it was most likely due to an external factor which they further suggest was likely climate change. The age when the global environmental effects of increased human population and economic development dominate planetary physical chemical and biological conditions 2. It had long been suspected that the quantity of threatened species today could be linked to the size density and growth of the human population.
Humans impact has been so profound that scientists have proposed that the Holocene era be declared over and the current epoch beginning in about 1900 be called the Anthropocene. Ending the current Holocene which began around 12000. In summary the mid-Holocene roughly 6000 years ago was generally warmer than today during summer in the Northern Hemisphere.
Between 6000 and 5600 cal. Second displacement of hunter-gatherers from south to north would. Expansion of the human enterprise during the Holocene and probably earlier eg.
Yr BP the summer climate substantially increased by 2 C in parallel with a 33 fold increase in population levels Fig. The population then declined after 106 ka but increased to a second peak at 915 ka which is only recorded in closed sites and may represent movement of people out of the basin into higher. Tallavaara and Seppä Reference Tallavaara and Seppä 2012.
The human population entered the region at 130 ka and grew to reach the first population peak at 107 ka during a period of high water at LOW from 113 to 104 ka. Human activity has transformed the Earths landscapes pervasively for thousands of years and the most important anthropogenic alteration was the clearing of forests and the establishment of agriculture.

Trends In Ancient Populations Osteobiography During The Holocene The Levantine Perspective

Late Pleistocene Early Holocene Climate Change The Upper Curve Download Scientific Diagram

Holocene Epoch An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Comparison Between Modelled Mid Holocene And Last Glacial Maximum Download Scientific Diagram

A Continuous Climatic Impact On Holocene Human Population In The Rocky Mountains Pnas

Trends In Ancient Populations Osteobiography During The Holocene The Levantine Perspective

Climate Past Present Future How Humans Are Influencing Climate Change And Its Significance In Defining A New Geological Epoch The Anthropocene

Abrupt Holocene Climate Shifts In Coastal East Asia Including The 8 2 Ka 4 2 Ka And 2 8 Ka Bp Events And Societal Responses On The Korean Peninsula Abstract Europe Pmc
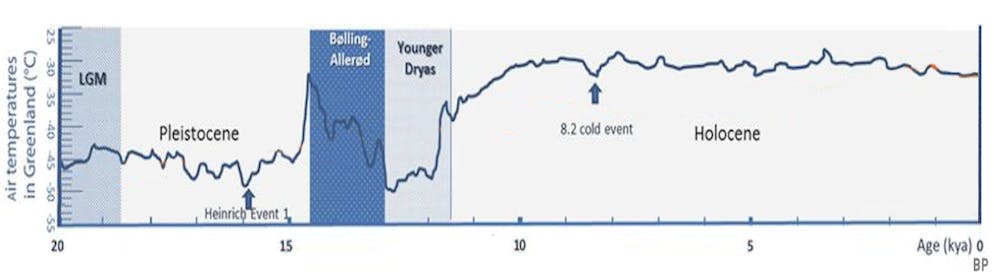
How Climate Change Affected Foraging Patterns Of Prehistoric Humans In Indonesia

Early Holocene An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Holocene Extinction Will Humans Be Able To Escape It

Temperature Deviations During The Past 45 000 Years As Shown In Download Scientific Diagram
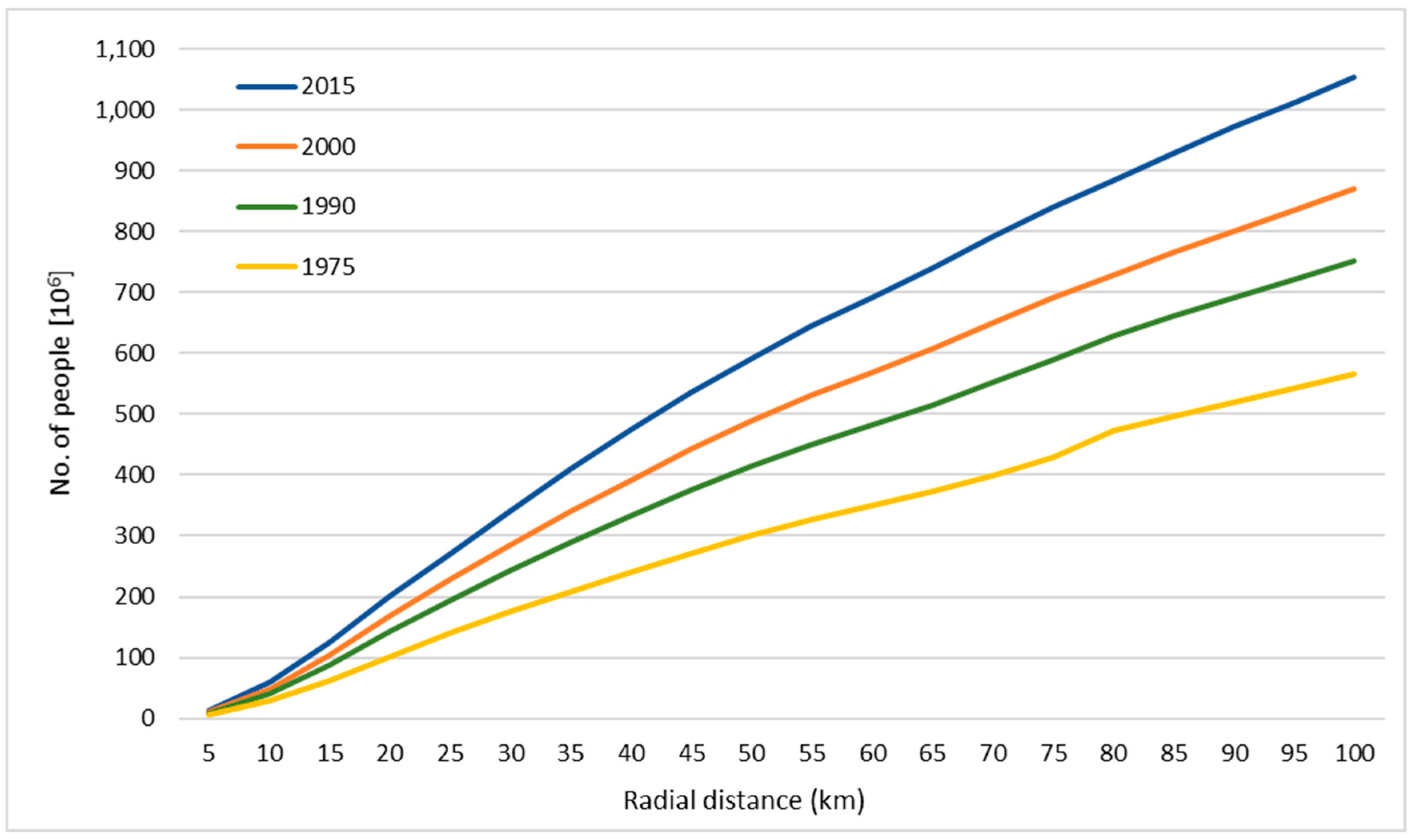
Ijgi Free Full Text An Improved Global Analysis Of Population Distribution In Proximity To Active Volcanoes 1975 2015 Html

Trends In Ancient Populations Osteobiography During The Holocene The Levantine Perspective

A Continuous Climatic Impact On Holocene Human Population In The Rocky Mountains Pnas

Vei 7 Eruptions During The Holocene And Global Population Recent Download Scientific Diagram

Comparison Of Key Trends In The Holocene And Anthropocene Adapted From Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment